Light Therapy Increases Brain Connectivity Following Injury
Safe, non-invasive intervention may potentially treat many neurological conditions



Low-level light therapy appears to affect healing in the brains of people who suffered significant brain injuries, according to a study published in Radiology.
Lights of different wavelengths have been studied for years for their wound-healing properties. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) conducted low-level light therapy on 38 patients who had suffered moderate traumatic brain injury. Patients received light therapy within 72 hours of their injuries through a helmet that emits near-infrared light.
“The skull is quite transparent to near-infrared light,” said study co-lead author Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD, from the Department of Radiology at MGH. “Once you put the helmet on, your whole brain is bathing in this light.”
The researchers used functional MRI to gauge the effects of the light therapy, focusing on the brain’s resting-state functional connectivity. They compared MRI results during three recovery phases: the acute phase of within one week after injury, the subacute phase of two to three weeks post-injury and the late-subacute phase of three months after injury.
Of the 38 patients in the trial, 21 did not receive light therapy while wearing the helmet. This was done to serve as a control to minimize bias due to patient characteristics and to avoid potential placebo effects.
Drs. Gupta, Mercaldo, Chan and Dr. Benjamin Vakoc, PhD, discuss their research on how low-level light therapy appears to affect healing in the brains of people who suffered significant brain injuries.
Patients who received low-level light therapy showed a greater change in resting-state connectivity in seven brain region pairs during the acute-to-subacute recovery phase compared to the control participants.
“There was increased connectivity in those receiving light treatment, primarily within the first two weeks,” said study coauthor Nathaniel Mercaldo, PhD, a statistician with MGH. “We were unable to detect differences in connectivity between the two treatment groups long term, so although the treatment appears to increase the brain connectivity initially, its long-term effects are still to be determined.”
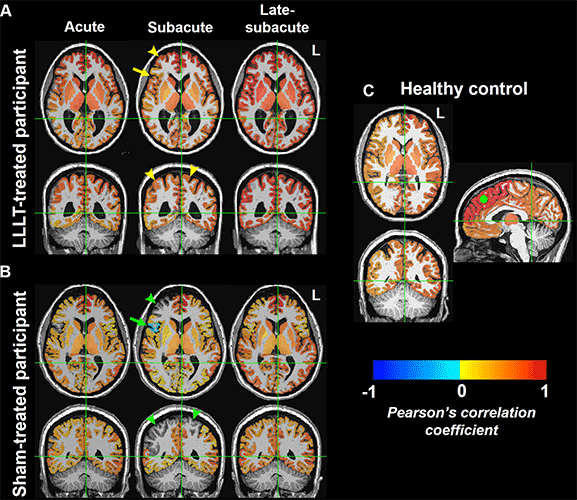
Functional MRI brain maps of resting-state functional connectivity in representative age- and sex-matched participants. (A, B) Axial (top) and coronal (bottom) views show whole-brain connectivity, with the seed at the left (L) superior frontal region, in a 36-year-old female participant in the low-level light therapy (LLLT) treatment group (A) and a 38-year-old female participant in the sham treatment group (B) during the acute, subacute, and late-subacute phases (columns, from left to right, in both A and B) of traumatic brain injury recovery. (C) Axial (top left), coronal (bottom left), and sagittal (right) views in a 38-year-old female control participant are shown for comparison; the solid green circle in the sagittal view indicates the location of the left superior frontal seed region. The color bar indicates that brain regions with warm colors (red, orange, yellow) show resting-state fluctuations that have significant positive correlation (r of 0 to 1) with those of the left superior frontal region, and brain regions with cold colors (blue) show resting-state fluctuations that have significant negative correlation (r of −1 to 0) with those of the left superior frontal region. Brain regions that have functional connectivity with the left superior frontal seed in the LLLT-treated participant (arrowheads in A) but not in the sham-treated participant (arrowheads in B) are shown. The arrow in A additionally shows brain regions with positive correlation with the seed in the LLLT-treated participant, but negative correlation with the seed in the sham-treated participant (arrow in B).
https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.230999 © RSNA 2024
Longer-term Evidence of Differences in Clinical Outcomes Still Needed
The precise mechanism of the light therapy’s effects on the brain is also still to be determined. Previous research points to the alteration of an enzyme in the cell’s mitochondria, Dr. Gupta said. This leads to more production of adenosine triphosphate, a molecule that stores and transfers energy in the cells. Light therapy has also been linked with blood vessel dilation and anti-inflammatory effects.
“There is still a lot of work to be done to understand the exact physiological mechanism behind these effects,” said study coauthor Suk-tak Chan, PhD, a biomedical engineer at MGH.
While connectivity increased for the light therapy-treated patients during the acute to subacute phases, there was no evidence of a difference in clinical outcomes between the treated and control participants. Additional studies with larger cohorts of patients and correlative imaging beyond three months may help determine the therapeutic role of light in traumatic brain injury.
The researchers expect the role of light therapy to expand as more study results come in. The 810-nanometer-wavelength light used in the study is already employed in various therapeutic applications. It’s safe, easy to administer and does not require surgery or medications. The helmet’s portability means it can be delivered in settings outside of the hospital. It may have applications in treating many other neurological conditions, according to Dr. Gupta.
“There are lots of disorders of connectivity, mostly in psychiatry, where this intervention may have a role,” he said. “PTSD, depression, autism: these are all promising areas for light therapy.”
For More Information
Access the Radiology study, “Effects of Low-Level Light Therapy on Resting-State Connectivity Following Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury: Secondary Analyses of a Double-blinded, Placebo-controlled Study.”
Read previous RSNA News stories about neuroimaging:
- Radiology Could Play a Bigger Role in the Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging and Brain PET Identify Neuroinflammation and AD in Overweight and Obese Persons
- Deep Learning Model Analyzes Head CT to Predict sTBI Patient Outcomes