RSNA Chynn Award for Neuroradiology Research Presented at RSNA 2021
Winning research uses MRI and AI to find mutations in tumors

Work on a biopsy alternative that combines MRI and artificial intelligence (AI) to noninvasively assess tumor biology has won the 2021 RSNA Kuo York Chynn Neuroradiology Research Award.
Tumor heterogeneity, the variation that exists among cells in a tumor, represents a major obstacle to effective cancer care. This heterogeneity is driven by frequent mutations in a tumor’s genome as it grows.
“Some mutations make tumors more resistant to radiation therapy and some make them more resistant to chemotherapy,” said Jason Parker, PhD, associate professor of radiology and imaging sciences at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis and this year’s Kuo York Chynn Neuroradiology Research Award recipient. “To develop highly effective treatments, we must identify and account for as many of the different mutations within a tumor as possible.”
Surgical biopsies don’t fully capture the heterogeneity of a tumor and taking multiple tissue samples is not feasible in such areas as the brain because of potential damage to surrounding tissue. A more effective, noninvasive way is needed to assess tumor heterogeneity and track changes in tumor genome over time.
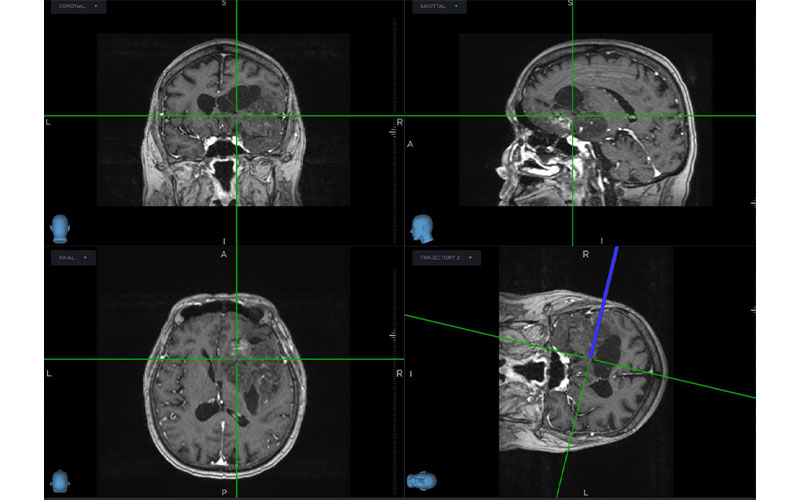
Identifying Genomic Mutations Can Create Personalized Cancer Treatment
Dr. Parker’s research centers on imaging tumors with a variety of MRI techniques and then applying deep learning to assess mutations in the exome, the portion of genome that codes for proteins. While the exome makes up only 1% to 2% of the genome, it is responsible for the vast majority of disease-causing genetic variants.
In a recent study, Dr. Parker and colleagues tested the method on eight patients with glioma. The patients underwent multiparametric MRI prior to surgery.
Before removing the tumors, a neurosurgeon biopsied different regions of them and used stereotaxis to record the tissue sample location. The researchers then obtained the exomic sequences from each sample and correlated those sequences with MRI features from different regions of the tumor. They deployed deep learning to sift through the genomic information from the whole-exome sequences.
Analysis showed that the combined AI-MRI approach had an accuracy rate of 80% in predicting mutations.
“We’re encouraged that in a small sample we can get reasonably accurate relationships between imaging characteristics and underlying genomic mutations present in whole-exome sequences,” Dr. Parker said.
Dr. Parker is currently developing a larger study of 30 patients to validate the results. The goal is to use imaging to map out different mutations in a tumor and then design treatments that target those mutations. Such a combined AI-MRI approach may permit treatment protocols to change quickly throughout the treatment as new mutations arise.
“If we can show that this combined AI-MRI methodology is generalizable to a broader population, it would represent an important advance in personalized cancer care,” Dr. Parker said.
Funded with a donation by internationally renowned neuroradiologist and longtime RSNA member Kuo York Chynn, MD, the RSNA Kuo York Chynn Neuroradiology Research Award provides $3,000 to the author of the top neuroradiology research paper presented at the RSNA annual meeting.
“I’m really excited and honored that our research was singled out like this,” Dr. Parker said. “It shows that there is a lot of interest right now in whole-exome sequencing being able to predict genomic aberrations from in vivo images, which we think is something that could really improve the treatment of cancer.”
For More Information
Access the RSNA 2021 session, “Mapping Whole Exome Sequencing To Noninvasive Imaging With Stereotactic Localization And Deep Learning,” at Meeting.RSNA.org.
Read about last year’s Chynn Neuroradiology Research Award winner in RSNA News: