Leaky Blood-Brain Barrier Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease
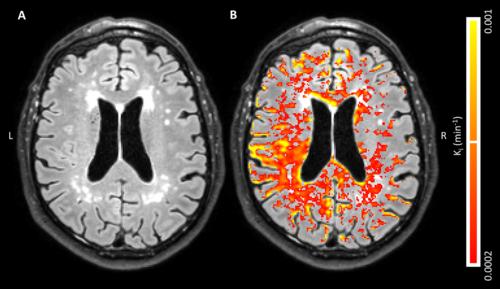
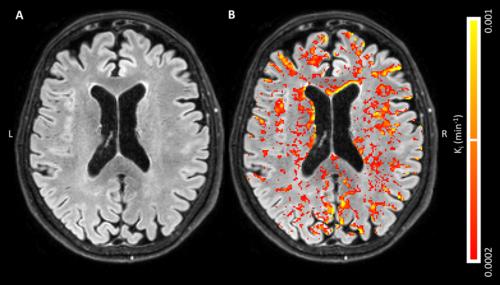
Global, diffusely distributed blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease (AD) suggests that a compromised BBB is part of the early pathology of AD and might be part of a cascade of pathologic events that eventually lead to cognitive decline, according to new Radiology research.
Harm J. van de Haar, MSc, of Maastricht University Medical Center in Maastricht, the Netherlands, and colleagues found that the BBB leakage rate was significantly higher in patients compared with that in control subjects in the total gray matter and cortex. For this pilot study, 16 patients with early AD and 17 healthy age-matched control subjects underwent dynamic contrast material–enhanced MRI sequence with dual time resolution for 25 minutes.
Patients had a significantly higher volume fraction of the leaking brain tissue in the GM, normal-appearing white matter, deep gray matter and cortex. When all subjects were considered, scores on the Mini-Mental State Examination decreased significantly with increasing leakage in the deep gray matter and cortex.
“We found an increased BBB leakage rate in the gray matter of patients with early AD. By also showing very subtle BBB impairment in the white matter, leakage volume proved to be even more sensitive to the differences in BBB leakage than was the leakage rate,” the authors write.
Web Extras
- Access the study, "Blood-Brain Barrier Leakage in Patients with Early Alzheimer Disease," at pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.2016152244